Modern agriculture involves fields of mind-boggling size, and spraying them efficiently is a serious operational challenge. Pyka[1] is taking on the largely human-powered spray business with an autonomous winged craft and, crucially, regulatory approval.
Just as we’ve seen with DroneSeed[2], this type of flying is risky for pilots, who must fly very close to the ground and other obstacles, yet also highly susceptible to automation; That’s because it involves lots of repetitive flight patterns that must be executed perfectly, over and over.
Pyka’s [3] approach is unlike that of many in the drone industry, which has tended to use multirotor craft for their maneuverability and easy take-off and landing. But those drones can’t carry the weight and volume of pesticides and other chemicals that (unfortunately) need to be deployed at large scales.

The craft Pyka has built is more traditional, resembling a traditional one-seater crop dusting plane but lacking the cockpit. It’s driven by a trio of propellers, and most of the interior is given over to payload (it can carry about 450 pounds) and batteries. Of course, there is also a sensing suite and onboard computer to handle the immediate demands of automated flight.
Pyka can take off or land on a 150-foot stretch of flat land, so you don’t have to worry about setting up a runway and wasting energy getting to the target area. Of course, it’ll eventually need to swap out batteries, which is part of the ground crew’s responsibilities. They’ll also be designing the overall course for the craft, though the actual flight path and moment-to-moment decisions are handled by the flight computer.
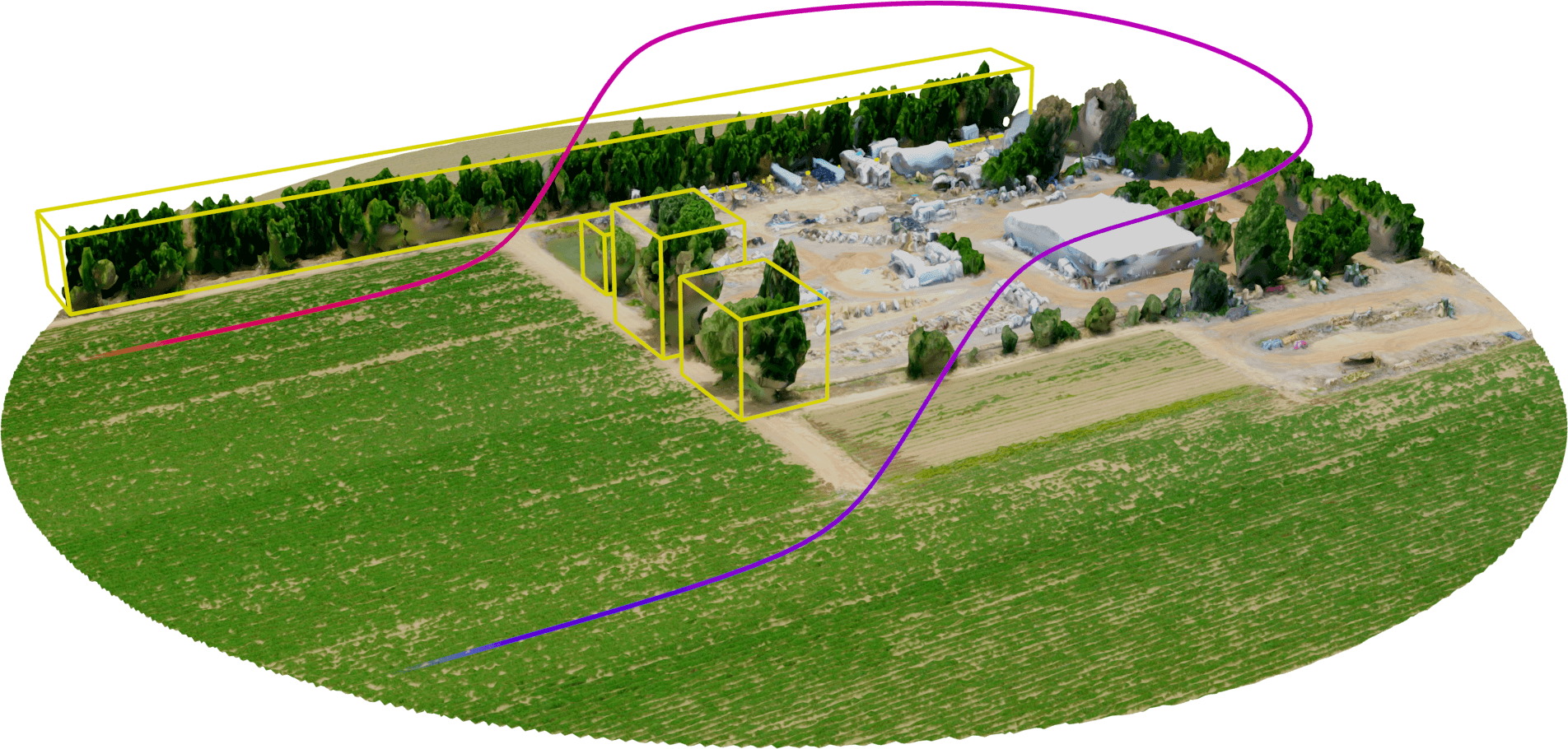
Example of a flight path accounting for obstacles without human input
All...